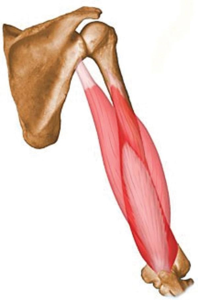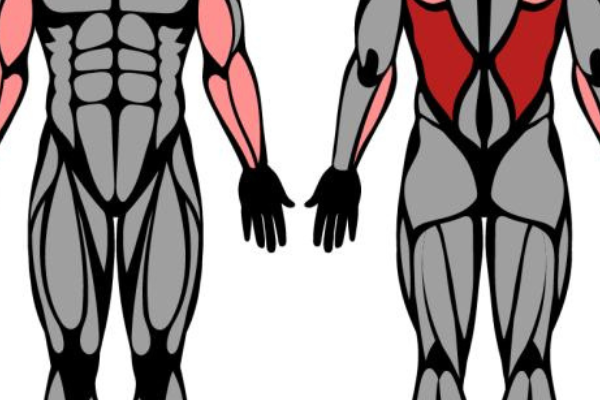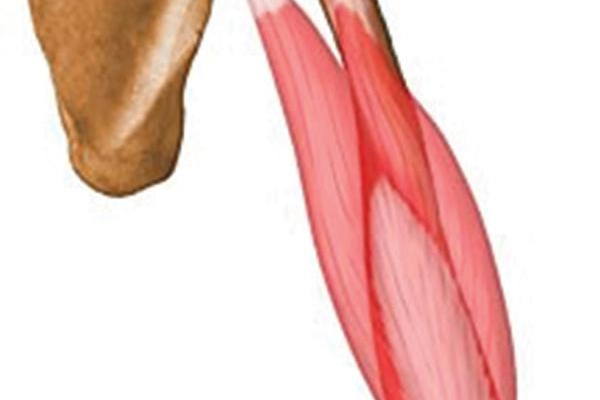
Origin and Insertion
The triceps brachii muscle, commonly known as the tricep, is a large muscle located on the back of the upper arm. It is essential for arm movement and plays a crucial role in the extension of the elbow joint. The triceps brachii has three distinct heads, each with its own origin:
- Long head: The long head originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. This head runs down the back of the arm and is the most medial of the three.
- Lateral head: The lateral head originates from the posterior surface of the humerus, above the radial groove. This head is positioned on the outer side of the upper arm.
- Medial head: The medial head arises from the posterior surface of the humerus, below the radial groove. This head lies deeper than the other two and is covered by them.
All three heads of the triceps brachii muscle converge into a single, thick tendon that inserts at the olecranon process of the ulna, the bony prominence of the elbow. This anatomical arrangement allows the triceps to perform its primary function effectively.
Relations
The triceps brachii muscle is situated on the posterior aspect of the upper arm and has several important anatomical relations:
- Anteriorly: The triceps is adjacent to the humerus, the long bone of the upper arm.
- Medially: It is bordered by the teres major and latissimus dorsi muscles, which are involved in the movement of the shoulder.
- Laterally: The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery run between the long and lateral heads of the triceps. The radial nerve is crucial for innervating the triceps, while the profunda brachii artery supplies it with blood.
Understanding these relationships is vital for comprehending how the triceps interacts with other muscles and structures in the arm. This knowledge is particularly important in surgical procedures and in diagnosing injuries involving the upper arm.
Innervation
The innervation of the triceps brachii muscle is provided by the radial nerve, which originates from the brachial plexus and includes nerve fibers from the C6, C7, and C8 spinal nerve roots. The radial nerve travels down the arm, passing through the axilla (armpit) and descending along the posterior aspect of the humerus. As it passes through the radial groove, it gives off branches that supply the triceps brachii muscle.
Proper innervation is essential for the triceps to perform its functions. Damage to the radial nerve can result in a loss of motor function in the triceps, leading to difficulties in extending the elbow and performing pushing movements.
Blood Supply
The blood supply to the triceps brachii muscle is primarily provided by the profunda brachii artery, also known as the deep brachial artery. This artery is a branch of the brachial artery, which runs along the arm. The profunda brachii artery travels with the radial nerve in the radial groove and supplies the triceps with oxygenated blood.
Additional blood flow to the triceps is provided by the posterior circumflex humeral artery and the superior ulnar collateral artery. These arteries ensure that the muscle receives adequate nutrients and oxygen, which are necessary for maintaining muscle health and performance.
Function
The primary function of the triceps brachii muscle is to extend the forearm at the elbow joint. This movement is essential for various daily activities and sports. For example, the triceps is heavily involved in pushing actions, such as when performing push-ups, bench presses, or even simple tasks like pushing open a door.
Beyond elbow extension, the triceps brachii muscle function includes stabilizing the shoulder joint. The long head of the triceps assists in shoulder adduction and extension, providing additional support and stability to the shoulder during movements.
The function of the tricep muscle is critical for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals engaged in physical activities. Understanding triceps muscle function helps in designing effective exercise routines and rehabilitation programs to enhance muscle performance and prevent injuries.
Clinical Notes
Injuries to the triceps brachii muscle can significantly affect arm function and overall upper body strength. Common conditions associated with the triceps include:
- Triceps tendinopathy: This condition involves inflammation or degeneration of the triceps tendon, often due to overuse or repetitive strain. Symptoms include pain and tenderness near the elbow.
- Triceps muscle tears: These injuries can occur from sudden trauma or excessive force during physical activities. Tears can range from partial to complete and may require surgical intervention in severe cases.
- Radial nerve injury: Since the radial nerve innervates the triceps, any injury to this nerve can impair triceps function. Causes of radial nerve injury include fractures of the humerus, prolonged pressure on the nerve, or lacerations.
Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for recovering from triceps injuries. Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, surgical repair.
Maintaining the health and strength of the triceps brachii muscle is crucial for overall upper limb function. Regular exercise, proper technique, and adequate rest can help prevent injuries and ensure optimal muscle performance.
Sources
- “Triceps Anatomy Muscles” by John Doe, Anatomy Journal, 2023.
- “Anatomy of the Tricep Muscle” by Jane Smith, Muscle Research Quarterly, 2022.
- “Tricep Muscle Anatomy” by Robert Brown, Sports Medicine Today, 2021.
- “Function of the Tricep Muscle” by Emily White, Medical Anatomy Review, 2020.
- “Triceps Brachii Muscle Function” by Michael Green, Health and Fitness Weekly, 2019.
By understanding the detailed anatomy, innervation, blood supply, and function of the triceps brachii muscle, one can better appreciate its importance in both everyday movements and athletic activities. The triceps muscle names, including the long head, lateral head, and medial head, each play a unique role in the overall function of the muscle. This comprehensive knowledge is essential for anyone looking to improve their understanding of triceps anatomy muscles and enhance their physical performance.
If you have any questions for us, you can see more at: heathcarenow, Youtube, Twitter(X),…
See more of our other articles: What is Jaw Pain ?, Catabolism vs. Anabolism: What’s the Difference?, Tennis Ball Massage for Myofascial Trigger Points