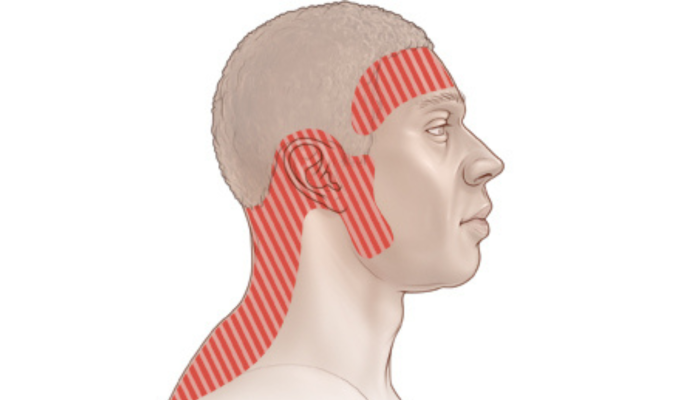
Causes
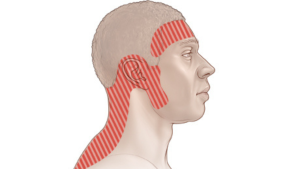
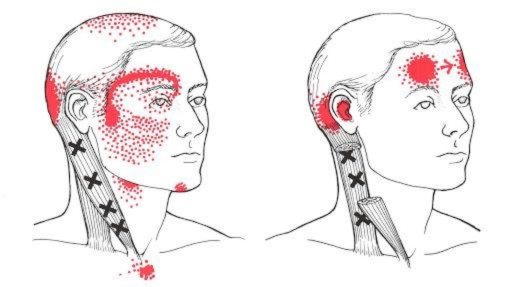
Tension headaches are among the most common types of headaches and are often linked to muscle tension and stress. A primary cause of tension headaches is muscle spasm in the head, which can result from physical or emotional strain. Muscle spasms in the back of the head, muscle twitching on the side of the head, or even muscle spasm on the side of the head can be indicative of tension. This tension can cause a tightening of the muscles in the scalp, leading to discomfort and pain.
Additionally, prolonged periods of poor posture or repetitive stress can contribute to these headaches. Muscle spasms in the head, especially around the scalp, are frequently associated with tension headaches. For some individuals, muscle spasm left side of the head or muscle spasm right side of the head may occur, but the underlying issue often remains the same: muscle tension and stress.
Symptoms
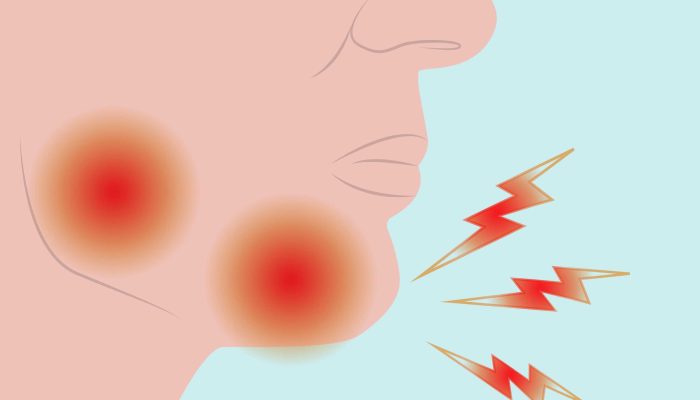
The symptoms of tension headaches typically include a dull, aching pain around the head. Many people describe it as a feeling of pressure or tightness, akin to having a tight band around the head. Muscle twitching in the head, muscle spasm on the scalp, or muscle twitching on the side of the head are common symptoms that accompany the headache.
Other signs can include:
- A constant ache or pressure in the forehead or the back of the head
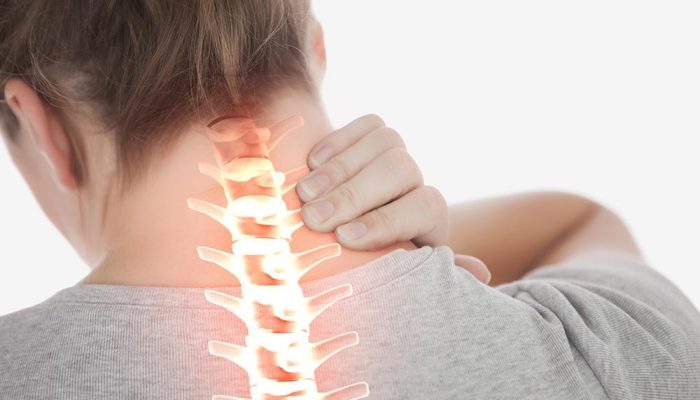
- Tenderness in the muscles of the neck, shoulders, or scalp
- Occasionally, a noticeable muscle twitch in the head or scalp muscle twitching may occur
Though these symptoms can be bothersome, they are typically not associated with more severe neurological conditions.
Exams and Tests
Diagnosing tension headaches usually involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers will often evaluate the pattern and severity of headaches and look for signs of muscle spasms in the head or muscle twitching on the scalp. They may also check for muscle twitching in the head and assess for any muscle spasm symptoms.
In some cases, if the headache symptoms are severe or persistent, additional tests might be necessary. These could include imaging studies such as a CT scan or MRI to rule out other causes of head pain, although these tests are generally not required for a typical tension headache diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for tension headaches focuses on relieving the pain and addressing the underlying muscle tension. Common strategies include:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate the pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: For severe cases, doctors may prescribe medications to help reduce muscle spasms in the head or muscle twitching in the scalp.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can relieve muscle tension and reduce symptoms of muscle spasm on the side of the head or muscle spasms in the back of the head.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, or yoga can be beneficial in managing stress, which is often a significant factor in tension headaches.
In cases where muscle spasms in the head are frequent or severe, addressing underlying stress or posture issues is crucial for long-term relief.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The prognosis for tension headaches is generally good. Most people experience relief with appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Muscle twitching head and muscle spasms in the head often decrease as stress levels decrease and muscle tension is managed. For some individuals, occasional tension headaches might persist, but with effective management strategies, they can usually be controlled.
It’s essential to follow a treatment plan and make necessary lifestyle changes to minimize the frequency and severity of these headaches. Persistent or worsening symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
While tension headaches are usually not a cause for alarm, it’s important to seek medical advice in certain situations. Contact a healthcare provider if:
- You experience severe or unusual pain
- You have a sudden onset of a headache with neurological symptoms
- Your headaches become more frequent or severe
- There is associated muscle twitching in head that is persistent or worsening
These signs may indicate a more serious condition that requires professional evaluation.
Prevention
Preventing tension headaches involves addressing the factors that contribute to muscle tension and stress. Effective strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce overall muscle tension and stress.
- Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture can prevent strain on neck and shoulder muscles.
- Stress Management: Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, can reduce stress levels and prevent headaches.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring sufficient, quality sleep can help manage stress and reduce muscle spasms in the head.
By implementing these preventative measures, individuals can effectively manage and reduce the frequency of tension headaches.
Tension Headache
Causes
Tension headaches are primarily caused by muscle tension in the head, neck, and shoulders. This tension often results from stress, poor posture, or muscle strain. Key factors include:
- Muscle Spasms: Muscle spasms in the head, such as muscle twitching on the side of the head or muscle spasm on the side of the head, are common. These spasms can create a sensation of tightness or pressure around the head.
- Muscle Tension: Prolonged stress or anxiety can lead to muscle tension, particularly in the scalp and neck. This tension may cause muscle spasms in the back of the head or muscle twitching in the scalp.
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing with poor posture for extended periods can strain neck and shoulder muscles, contributing to muscle spasms in the head and tension headaches.
- Emotional Stress: High levels of stress and anxiety can cause muscle spasms and tightness in the head, leading to tension headaches.
Understanding these causes can help in managing and preventing tension headaches.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tension headaches can vary but typically include:
- Dull, Aching Pain: A consistent, dull ache around the head, often described as a feeling of pressure or tightness.
- Muscle Spasms: Noticeable muscle spasms in the head, such as muscle twitching in the head or muscle spasm left side of the head.
- Tenderness: Tenderness in the muscles of the neck, shoulders, or scalp.
- Muscle Twitching: Occasional muscle twitching on the scalp or muscle twitching on the side of the head.
These symptoms can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Recognizing them can aid in timely treatment.
Exams and Tests
To diagnose tension headaches, healthcare providers typically:
- Review Medical History: Discuss symptoms, frequency, and potential triggers.
- Perform Physical Examination: Assess for muscle spasms in the head, muscle twitching on the side of the head, and other physical signs.
- Conduct Additional Tests: If necessary, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs may be used to exclude other causes of headaches, though these are rarely needed for standard tension headaches.
A thorough examination helps in distinguishing tension headaches from other types of headaches and ensures appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Managing tension headaches involves both short-term relief and long-term strategies:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain. In more severe cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to address muscle spasms in the head.
- Physical Therapy: Techniques to improve posture and reduce muscle tension can be beneficial. Stretching and strengthening exercises help alleviate muscle spasms in the back of the head and improve overall neck and shoulder health.
- Stress Management: Implementing stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can reduce the frequency and intensity of tension headaches.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a regular exercise routine, practicing good posture, and ensuring adequate sleep can prevent the recurrence of tension headaches.
Effective treatment often requires a combination of these approaches tailored to individual needs.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook for tension headaches is generally positive. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals experience significant relief. Key points include:
- Effective Management: Many people find relief through a combination of medication, physical therapy, and stress management.
- Chronic Cases: For those with chronic or frequent tension headaches, ongoing management strategies are essential to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Improvement with Time: Symptoms typically improve with proper treatment and preventive measures, though occasional headaches may still occur.
Understanding the prognosis helps set realistic expectations and encourages proactive management of symptoms.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical attention if:
- Severe Pain: Headaches are severe, sudden, or different from usual headaches.
- Neurological Symptoms: New neurological symptoms, such as vision changes or weakness, accompany the headache.
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: Headaches become more frequent, intense, or resistant to over-the-counter treatments.
- Significant Muscle Spasms: Persistent muscle spasms in the head or significant muscle twitching in the scalp.
Consulting a healthcare provider ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if symptoms change or worsen.
Prevention
Preventive strategies can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of tension headaches:
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps reduce overall muscle tension and stress.
- Good Posture: Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and using electronic devices.
- Stress Reduction: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your routine to manage stress effectively.
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Aim for consistent, quality sleep to help reduce tension and prevent headaches.
By incorporating these preventive measures, individuals can manage tension headaches more effectively and improve overall well-being.
If you have any questions for us, you can see more at: heathcarenow, Youtube, Twitter(X),…
See more of our other articles: What is Jaw Pain ?, Catabolism vs. Anabolism: What’s the Difference?, Tennis Ball Massage for Myofascial Trigger Points