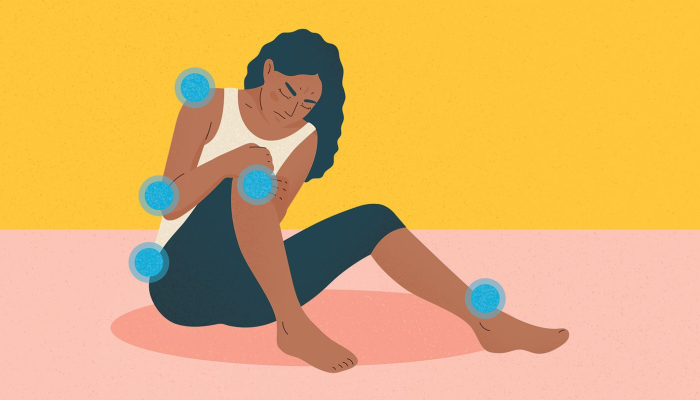
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also cause a wide range of systemic symptoms and complications. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear, RA is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling. One of the frequently asked questions by those diagnosed with RA is: can rheumatoid arthritis cause muscle pain? Understanding the diverse symptoms and potential complications is essential for managing this complex disease effectively.
Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The early signs of RA can be subtle and may develop gradually. They often include:
- Joint pain and swelling: Commonly affecting the small joints in the hands and feet, this pain is typically symmetrical, meaning it occurs in the same joints on both sides of the body.
- Morning stiffness: This can last for hours and is one of the hallmark symptoms of RA.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or fatigued is common and can be severe.
- Fever and weight loss: Some people with RA may experience a low-grade fever and unintended weight loss.
- Rheumatoid nodules: These are firm lumps of tissue under the skin, often near the elbows.
These symptoms can come and go, with periods of increased disease activity (flares) and periods of relative remission.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Joints
RA primarily targets the synovial joints, which are the most movable type of joint in the body. As the disease progresses, it can affect larger joints, including:
- Knees: Inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
- Ankles: RA can cause pain and swelling in the ankles, affecting mobility.
- Elbows: Inflammation can lead to pain and a limited range of motion.
- Hips: Although less common, RA can cause hip pain and stiffness.
- Shoulders: Inflammation can lead to pain and difficulty with arm movements.
The ongoing inflammation can eventually cause joint damage and deformity if not adequately managed.
Whole-Body Effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
RA is a systemic disease, meaning it can affect the entire body. One significant concern for RA patients is can rheumatoid arthritis cause muscle pain? The answer is yes. In addition to joint pain, RA can cause widespread muscle pain and weakness due to chronic inflammation and decreased physical activity. Other whole-body effects include:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease: Chronic inflammation can lead to a higher risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Lung disease: RA can cause various lung problems, including interstitial lung disease and pleurisy.
- Osteoporosis: RA and some of its treatments can increase the risk of osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones.
Skin Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
The skin can also be affected by RA. Common skin symptoms include:
- Rheumatoid nodules: These firm lumps can develop under the skin near affected joints. They are usually painless but can become tender.
- Rashes and ulcers: Inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) can lead to skin rashes and ulcers, particularly on the legs.
Skin symptoms may indicate more severe disease activity and require medical attention.
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Your Lungs
RA can lead to several lung-related issues, such as:
- Interstitial lung disease: This condition involves inflammation and scarring of the lung tissue, leading to shortness of breath and a persistent dry cough.
- Lung nodules: Small lumps can form in the lungs, which are typically benign but require monitoring.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lining around the lungs can cause sharp chest pain, especially when breathing deeply.
Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial to manage these lung complications effectively.
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Your Heart
RA increases the risk of heart problems, including:
- Cardiovascular disease: Chronic inflammation can damage the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining around the heart can cause chest pain and other symptoms.
- Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle can lead to heart failure if untreated.
Regular cardiovascular screening is important for RA patients to identify and manage these risks early.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Eye Symptoms
RA can affect the eyes, leading to several conditions:
- Dry eyes: Reduced tear production can cause discomfort and increase the risk of eye infections.
- Scleritis: Inflammation of the white part of the eye can cause severe pain and redness.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the middle layer of the eye can lead to pain, redness, and vision problems.
Eye symptoms require prompt evaluation and treatment by an eye specialist.
Other Body Parts Rheumatoid Arthritis Can Affect
Beyond the joints, lungs, heart, and eyes, RA can affect other parts of the body, including:
- Kidneys: RA and its treatments can affect kidney function.
- Blood vessels: Vasculitis, an inflammation of the blood vessels, can reduce blood supply to tissues and organs, potentially leading to damage.
- Nervous system: RA can cause nerve pain and damage, leading to symptoms like numbness and tingling.
It’s essential for RA patients to have regular check-ups to monitor and manage these potential complications.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Your Mental Health
Living with RA can take a significant toll on mental health. Chronic pain, physical limitations, and the stress of managing a long-term illness can lead to:
- Depression: Persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities.
- Anxiety: Increased worry and fear about the future and disease progression.
- Fatigue: Physical and emotional exhaustion that can worsen mental health symptoms.
Support from mental health professionals, support groups, and loved ones can be crucial in managing these challenges.
Track Your Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Keeping a detailed record of your symptoms can help you and your healthcare provider better understand the progression of RA and the effectiveness of treatments. Note the severity and frequency of joint pain, muscle pain, fatigue, and any other symptoms. This information can be invaluable in tailoring your treatment plan to your specific needs. Consider using a symptom tracker app or a journal to record daily symptoms and triggers.
Takeaways
RA is a complex and systemic disease that requires a comprehensive approach to management. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing joint damage and systemic complications. Awareness of the wide range of symptoms, including the potential for muscle pain and weakness, can help patients seek timely medical attention and improve their overall prognosis.
RA Symptoms FAQs
Can rheumatoid arthritis cause muscle pain? Yes, the inflammation from RA can cause muscle pain and weakness.
Does rheumatoid arthritis affect muscles and tendons? Yes, RA can affect both muscles and tendons, leading to pain and decreased function.
Can RA cause muscle spasms? Yes, RA can cause muscle spasms due to inflammation and nerve irritation.
What are common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis? Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, fatigue, and systemic effects such as lung and heart involvement.
How does RA affect the body beyond the joints? RA can affect the skin, lungs, heart, eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, and nervous system, leading to a wide range of complications.
How can I manage muscle pain related to RA? Management may include medication, physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Consulting with a healthcare provider for a tailored treatment plan is essential.
What are the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis? Early signs include tender, warm, swollen joints, morning stiffness, fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
Is mental health affected by rheumatoid arthritis? Yes, chronic pain and physical limitations can lead to depression and anxiety. Mental health support is an important part of RA management.
Can rheumatoid arthritis cause muscle weakness? Yes, RA can cause muscle weakness due to chronic inflammation and reduced physical activity.
What should I do if I experience new symptoms or worsening of existing symptoms? Contact your healthcare provider for an evaluation and to discuss potential adjustments to your treatment plan.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of RA, including its potential to cause muscle pain, is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life. Regular communication with healthcare providers and staying informed about the disease can help patients navigate the challenges of living with RA.
If you have any questions for us, you can see more at: heathcarenow, Youtube, Twitter(X),…