WHAT IS THE BRACHIALIS MUSCLE AND WHAT DOES IT DO?
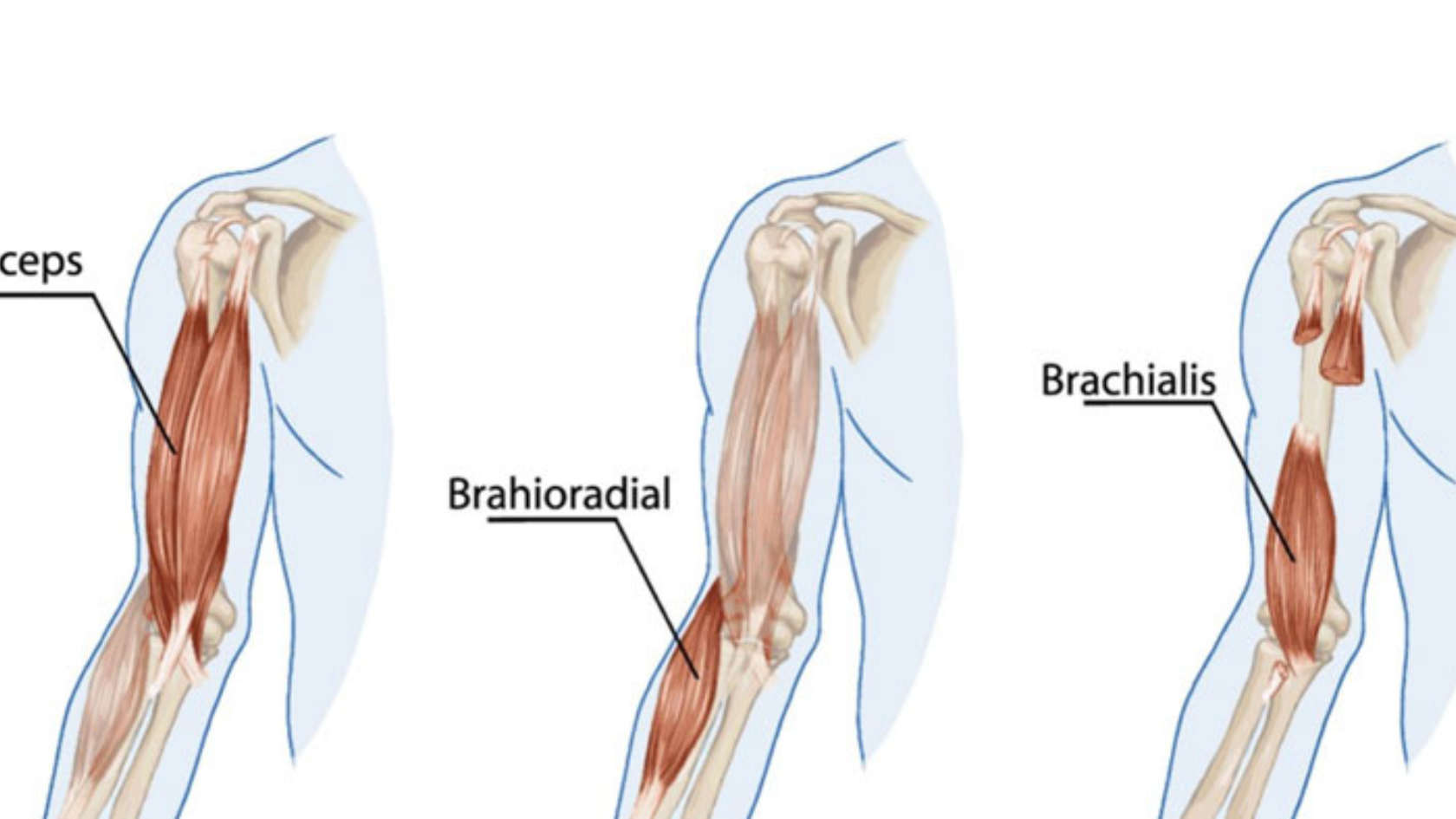
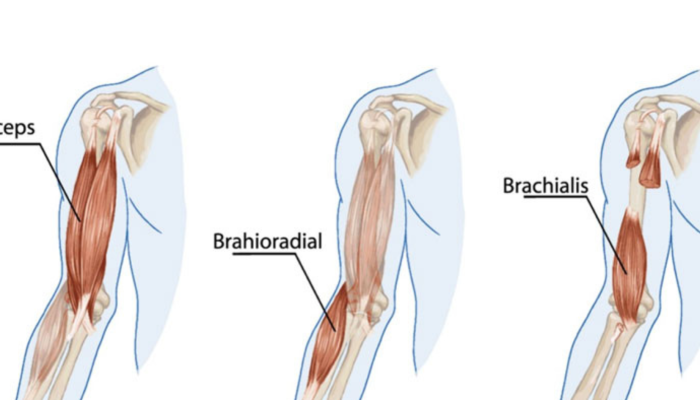
The brachialis muscle is a key player in arm movement, located underneath the biceps brachii on the front part of the upper arm. Its primary function is elbow flexion, which allows for the bending of the arm at the elbow. This muscle is crucial for activities involving lifting and carrying, making it essential for both daily tasks and athletic movements. Understanding its role highlights the importance of maintaining its health and addressing any pain in the brachialis muscle promptly.
WHAT CAUSES BRACHIALIS STRAIN?
A brachialis strain typically occurs due to overuse or excessive force applied during activities that require repetitive or intense elbow flexion. Common causes include weightlifting, especially exercises like curls, and sports that involve throwing or hitting motions. An unexpected impact or sudden increase in activity intensity can also lead to a strain. Recognizing these causes helps in preventing injuries and understanding the importance of proper training and conditioning.
SYMPTOMS OF BRACHIALIS STRAIN
Identifying a brachialis strain involves noting several key symptoms:
- Pain in the brachialis muscle: This is often the most immediate and noticeable symptom, felt on the front part of the upper arm.
- Swelling and tenderness: The area around the muscle may become swollen and sensitive to touch.
- Reduced strength: There may be noticeable weakness in the arm, especially when attempting to flex the elbow.
- Limited range of motion: Movement at the elbow can be restricted due to pain and discomfort.
These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, making it essential to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
OTHER CONDITIONS SIMILAR TO BRACHIALIS STRAIN
Several other conditions may present similar symptoms to a brachialis strain, including:
- Brachioradialis muscle pain: This muscle, located in the forearm, can also experience strain, leading to pain that might be confused with brachialis issues.
- Biceps tendinitis: Inflammation of the biceps tendon can cause pain in the same general area.
- Torn brachialis muscle: A more severe injury where the muscle fibers are partially or completely torn, causing intense pain and dysfunction.
Distinguishing between these conditions requires careful examination and sometimes imaging studies by a healthcare professional.
WHO IS AT RISK OF EXPERIENCING BRACHIALIS STRAIN?
Certain individuals are more prone to experiencing brachialis strain, including:
- Athletes: Especially those involved in weightlifting, bodybuilding, or sports that require repetitive arm movements.
- Manual laborers: Jobs that require frequent lifting and carrying can increase the risk.
- Older adults: Age-related muscle weakening can make strains more likely.
- Individuals with poor training techniques: Incorrect form during exercises can place undue stress on the brachialis muscle.
Awareness of these risk factors can help in taking preventive measures and seeking early intervention.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR BRACHIALIS STRAIN
Treating a brachialis strain involves several strategies to promote healing and restore function:
- Rest and ice: Initially, resting the affected arm and applying ice can reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression and elevation: Using a compression bandage and elevating the arm can help manage inflammation.
- Pain relief medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide relief from pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Guided exercises and stretches can aid in recovery and prevent future injuries.
PAIN RELIEF TIPS
In addition to medical treatments, several pain relief tips can help manage discomfort:
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain: Resting the muscle is crucial for recovery.
- Using heat therapy: Applying heat can relax the muscle and improve blood flow after the initial swelling has subsided.
- Gentle stretching: Light stretching exercises can maintain flexibility without overloading the muscle.
HOW PHYSIOTHERAPY CAN HELP PEOPLE WITH BRACHIALIS STRAIN
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in recovering from a brachialis strain. A physiotherapist can develop a personalized treatment plan that includes:
- Strengthening exercises: Targeted exercises to rebuild muscle strength and prevent future injuries.
- Flexibility training: Stretching routines to maintain and improve the range of motion.
- Manual therapy: Techniques such as massage and mobilization to reduce pain and enhance tissue healing.
- Education: Guidance on proper techniques and ergonomics to avoid further strain.
In conclusion, addressing brachialis muscle pain through a combination of rest, targeted treatment, and physiotherapy can effectively manage symptoms and promote recovery. Prioritizing early intervention and adhering to a structured physiotherapy program can significantly enhance outcomes and prevent recurrent injuries.
Physiotherapy sessions not only focus on healing but also on educating individuals about proper techniques and body mechanics to prevent recurrence of the injury. By understanding the underlying causes and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can continue their activities with reduced risk of future brachialis strains. Here are some more detailed aspects of how physiotherapy can assist in the recovery process:
Customized Exercise Programs
Physiotherapists design exercise programs tailored to the individual’s specific condition and recovery stage. These programs typically include:
- Isometric exercises: Initially, isometric exercises help in maintaining muscle strength without causing further strain.
- Progressive resistance exercises: Gradually increasing resistance helps in rebuilding muscle strength and endurance.
- Functional training: Exercises that mimic daily activities and sports-specific movements to ensure the muscle can handle real-life demands.
Pain Management Techniques
Physiotherapists employ various techniques to manage pain, such as:
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): This method uses electrical currents to reduce pain and improve muscle function.
- Ultrasound therapy: High-frequency sound waves promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
- Soft tissue mobilization: Hands-on techniques to improve circulation and relieve muscle tightness.
Education and Preventive Strategies
An essential part of physiotherapy is educating the patient on how to avoid future injuries. This includes:
- Proper lifting techniques: Learning the correct way to lift objects to minimize strain on the brachialis and other muscles.
- Ergonomic advice: Adjusting workspaces and tools to reduce unnecessary strain.
- Warm-up and cool-down routines: Incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down exercises to prepare the muscles for activity and aid in recovery.
Nutritional Guidance
Though not always directly within the physiotherapist’s scope, they may provide general advice or refer to a nutritionist. Proper nutrition supports muscle repair and overall recovery. Adequate protein intake, hydration, and vitamins like vitamin C and D are crucial for muscle health.
Psychological Support
Dealing with an injury can be mentally taxing. Physiotherapists often provide support and motivation, helping individuals stay positive and focused on their recovery goals. Techniques such as mindfulness and stress management can also be beneficial.
Long-Term Rehabilitation
For severe cases, long-term rehabilitation might be necessary. This can include ongoing physiotherapy sessions to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. The goal is to ensure a full return to normal activities without pain or limitations.
Case Study: Successful Recovery
Consider the case of John, a 35-year-old weightlifter who experienced a brachialis strain. John’s physiotherapist created a comprehensive plan that included initial rest and ice application, followed by progressive exercises. With a combination of manual therapy, education on proper lifting techniques, and consistent follow-up sessions, John successfully returned to his weightlifting regimen pain-free within three months. This highlights the importance of a structured and personalized approach to physiotherapy.
Conclusion
Dealing with a brachialis strain requires a multifaceted approach involving rest, targeted treatment, and a structured physiotherapy program. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can effectively manage and overcome this condition. Physiotherapy not only aids in immediate recovery but also equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to prevent future injuries, ensuring long-term muscle health and function.
If you have any questions for us, you can see more at: heathcarenow, Youtube, Twitter(X),…
See more of our other articles: What is Jaw Pain ?, Catabolism vs. Anabolism: What’s the Difference?, Tennis Ball Massage for Myofascial Trigger Points